If you are running Ubuntu via WSL (Windows Subsystem for Linux) and wish to connect to the MySQL instance on the host machine, you will need to use the host machine’s IPv4 address e.g. 192.X.X.X, not 127.0.0.1 or localhost.
$ mysql -u <user> -h 127.0.0.1 -p -P 3306
ERROR 2003 (HY000): Can't connect to MySQL server on '127.0.0.1:3306' (111)
$ mysql -u <user> -h 192.X.X.X -p -P 3306
Welcome to the MySQL monitor...Server version: 8.0.26 MySQL Community Server - GPL
Copyright (c) 2000, 2022, Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Type 'help;' or 'h' for help. Type 'c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql>
To check your IPv4 address, go to Settings -> Network $ Internet -> Properties -> IPv4 address.
I got the same error configuring MySQL URI for apache airflow as:
mysql+mysqlconnector://<user>:<password>@localhost:3306/<database>
(mysql.connector.errors.DatabaseError) 2003 (HY000): Can't connect to MySQL server on 'localhost:3306' (111)
or
mysql+mysqlconnector://<user>:<password>@127.0.0.1:3306/<database>
(mysql.connector.errors.DatabaseError) 2003 (HY000): Can't connect to MySQL server on '127.0.0.1:3306' (111)
Fixed the error configuring the URI as:
mysql+mysqlconnector://<user>:<password>@192.X.X.X:3306/<database>
If you are running Ubuntu via WSL (Windows Subsystem for Linux) and wish to connect to the MySQL instance on the host machine, you will need to use the host machine’s IPv4 address e.g. 192.X.X.X, not 127.0.0.1 or localhost.
$ mysql -u <user> -h 127.0.0.1 -p -P 3306
ERROR 2003 (HY000): Can't connect to MySQL server on '127.0.0.1:3306' (111)
$ mysql -u <user> -h 192.X.X.X -p -P 3306
Welcome to the MySQL monitor...Server version: 8.0.26 MySQL Community Server - GPL
Copyright (c) 2000, 2022, Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Type 'help;' or 'h' for help. Type 'c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql>
To check your IPv4 address, go to Settings -> Network $ Internet -> Properties -> IPv4 address.
I got the same error configuring MySQL URI for apache airflow as:
mysql+mysqlconnector://<user>:<password>@localhost:3306/<database>
(mysql.connector.errors.DatabaseError) 2003 (HY000): Can't connect to MySQL server on 'localhost:3306' (111)
or
mysql+mysqlconnector://<user>:<password>@127.0.0.1:3306/<database>
(mysql.connector.errors.DatabaseError) 2003 (HY000): Can't connect to MySQL server on '127.0.0.1:3306' (111)
Fixed the error configuring the URI as:
mysql+mysqlconnector://<user>:<password>@192.X.X.X:3306/<database>
This tutorial is intended to explain the necessary steps for solving the “ERROR 2003 (HY000): Can’t connect to MySQL server on ‘127.0.0.1’ (111)” which might occur when you try to access the MySQL database server.
Before moving any further, if you are a Linux user who is new to MySQL/MariaDB, then you may consider learning MySQL / MariaDB for Beginners – Part 1 and 20 MySQL (Mysqladmin) Commands for Database Administration in Linux as well.
On the other hand, if you are already a intermediate/experienced MySQL user, you can master these 15 Useful MySQL/MariaDB Performance Tuning and Optimization Tips.
Note: For this tutorial, it is assumed that you have already installed mysql database server.
Coming back to the point of focus, what are some of the possible causes of this error?
- Network failure especially if mysql database server is running on remote host.
- No mysql server is running on the mentioned host.
- Firewall blocking TCP-IP connection or other related reasons.
Below are the essential steps to deal with it.
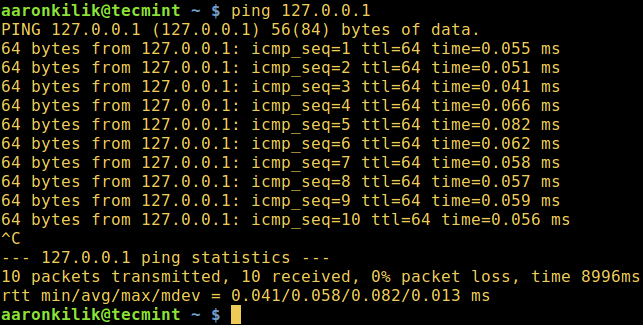
1. If database server is on a remote machine, then try to test the client-server connectivity using ping command, for instance:
$ ping server_ip_address
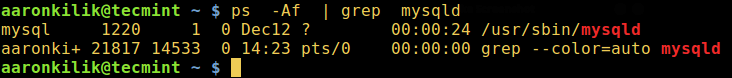
Once there is connectivity, use the ps command below which shows information about a selection of the active processes, together with a pipe and grep command, to check that the mysql daemon is running on your system.
$ ps -Af | grep mysqld
where the option:
-A– activates selection of all processes-f– enables full format listing
If there is no output from the previous command, start the mysql service as follows:
$ sudo systemctl start mysql.service $ sudo systemctl start mariadb.service OR # sudo /etc/init.d/mysqld start
After starting mysql service, try to access the database server:
$ mysql -u username -p -h host_address
2. If you still get the same error, then determine the port (default is 3306) on which the mysql daemon is listening by running the netstat command.
$ netstat -lnp | grep mysql
where the options:
-l– displays listening ports-n– enables display of numerical addresses-p– shows PID and name of the program owning the socket
Therefore use the -P option to specify the port you see from the output above while accessing the database server:
$ mysql -u username -p -h host_address -P port
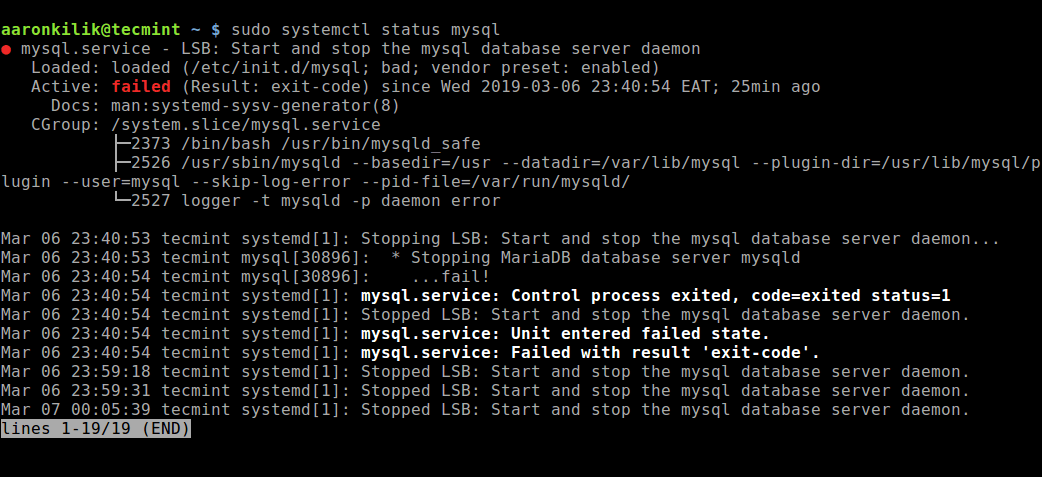
3. If all the above commands run successfully, but you still see the error, open the mysql config file.
$ vi /etc/mysql/my.cnf OR $ vi /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnf
Look for the line below and comment it out using the # character:
bind-address = 127.0.0.1
Save the file and exit, afterwards restart the mysql service like so:
$ sudo systemctl start mysql.service $ sudo systemctl start mariadb.service OR # sudo /etc/init.d/mysqld start
However, if you have firewallD or Iptables running try to review firewall services and open the mysql port, assuming it is firewall blocking TCP-IP connections to your mysql server.
That’s all! Do you know other methods or have suggestions for solving the MySQL connection error above? Let us know by dropping a comment via the feedback form below.
If You Appreciate What We Do Here On TecMint, You Should Consider:
TecMint is the fastest growing and most trusted community site for any kind of Linux Articles, Guides and Books on the web. Millions of people visit TecMint! to search or browse the thousands of published articles available FREELY to all.
If you like what you are reading, please consider buying us a coffee ( or 2 ) as a token of appreciation.
We are thankful for your never ending support.
MySQL — система управления базами данных (СУБД) с открытым исходным кодом от компании Oracle. Она была разработана и оптимизирована специально для работы веб-приложений. MySQL является неотъемлемой частью таких веб-сервисов, как Facebook, Twitter, Wikipedia, YouTube и многих других.
Эта статья расскажет, как определять, с чем связаны частые ошибки на сервере MySQL, и устранять их.
Не удаётся подключиться к локальному серверу
Одной из распространённых ошибок подключения клиента к серверу является «ERROR 2002 (HY000): Can’t connect to local MySQL server through socket ‘/var/run/mysqld/mysqld.sock’ (2)».
Эта ошибка означает, что на хосте не запущен сервер MySQL (mysqld) или вы указали неправильное имя файла сокета Unix или порт TCP/IP при попытке подключения.
Убедитесь, что сервер работает. Проверьте процесс с именем mysqld на хосте сервера, используя команды ps или grep, как показано ниже.
$ ps xa | grep mysqld | grep -v mysqldЕсли эти команды не показывают выходных данных, то сервер БД не работает. Поэтому клиент не может подключиться к нему. Чтобы запустить сервер, выполните команду systemctl.
$ sudo systemctl start mysql #Debian/Ubuntu
$ sudo systemctl start mysqld #RHEL/CentOS/FedoraЧтобы проверить состояние службы MySQL, используйте следующую команду:
$ sudo systemctl status mysql #Debian/Ubuntu
$ sudo systemctl status mysqld #RHEL/CentOS/FedoraЕсли в результате выполнения команды произошла ошибка службы MySQL, вы можете попробовать перезапустить службу и ещё раз проверить её состояние.
$ sudo systemctl restart mysql
$ sudo systemctl status mysqlЕсли сервер работает (как показано) и вы по-прежнему видите эту ошибку, вам следует проверить, не заблокирован ли порт TCP/IP брандмауэром или любой другой службой блокировки портов.
Для поиска порта, который прослушивается сервером, используйте команду netstat.
$ sudo netstat -tlpn | grep "mysql"Ещё одна похожая и часто встречающаяся ошибка подключения — «(2003) Can’t connect to MySQL server on ‘server’ (10061)». Это означает, что в сетевом соединении было отказано.
Следует проверить, работает ли в системе сервер MySQL (смотрите выше) и на тот ли порт вы подключаетесь (как найти порт, можно посмотреть выше).
Похожие частые ошибки, с которыми вы можете столкнуться при попытке подключиться к серверу MySQL:
ERROR 2003: Cannot connect to MySQL server on 'host_name' (111)
ERROR 2002: Cannot connect to local MySQL server through socket '/tmp/mysql.sock' (111)В MySQL учётная запись (УЗ) определяется именем пользователя и клиентским хостом, с которого пользователь может подключиться. УЗ может также иметь данные для аутентификации (например, пароль).
Причин для запрета доступа может быть много. Одна из них связана с учётными записями MySQL, которые сервер разрешает использовать клиентским программам при подключении. Это означает, что имя пользователя, указанное в соединении, может не иметь прав доступа к базе данных.
В MySQL есть возможность создавать учётные записи, позволяющие пользователям клиентских программ подключаться к серверу и получать доступ к данным. Поэтому при ошибке доступа проверьте разрешение УЗ на подключение к серверу через клиентскую программу.
Увидеть разрешённые привилегии учётной записи можно, выполнив в консоли команду SHOW GRANTS
Входим в консоль (пример для Unix, для Windows консоль можно найти в стартовом меню):
В консоли вводим команду:
> SHOW GRANTS FOR 'tecmint'@'localhost';Дать привилегии конкретному пользователю в БД по IP-адресу можно, используя следующие команды:
> grant all privileges on *.test_db to 'tecmint'@'192.168.0.100';
> flush privileges;Ошибки запрещённого доступа могут также возникнуть из-за проблем с подключением к MySQL (см. выше).
Потеря соединения с сервером MySQL
С этой ошибкой можно столкнуться по одной из следующих причин:
- плохое сетевое соединение;
- истекло время ожидания соединения;
- размер BLOB больше, чем
max_allowed_packet.
В первом случае убедитесь, что у вас стабильное сетевое подключение (особенно, если подключаетесь удалённо).
Если проблема с тайм-аутом соединения (особенно при первоначальном соединении MySQL с сервером), увеличьте значение параметра connect_timeout.
В случае с размером BLOB нужно установить более высокое значение для max_allowed_packet в файле конфигурации /etc/my.cnf в разделах [mysqld] или [client] как показано ниже.
[mysqld]
connect_timeout=100
max_allowed_packet=500MЕсли файл конфигурации недоступен, это значение можно установить с помощью следующей команды.
> SET GLOBAL connect_timeout=100;
> SET GLOBAL max_allowed_packet=524288000;Слишком много подключений
Эта ошибка означает, что все доступные соединения используются клиентскими программами. Количество соединений (по умолчанию 151) контролируется системной переменной max_connections. Устранить проблему можно, увеличив значение переменной в файле конфигурации /etc/my.cnf.
[mysqld]
max_connections=1000Недостаточно памяти
Если такая ошибка возникла, это может означать, что в MySQL недостаточно памяти для хранения всего результата запроса.
Сначала нужно убедиться, что запрос правильный. Если это так, то нужно выполнить одно из следующих действий:
- если клиент MySQL используется напрямую, запустите его с ключом
--quick switch, чтобы отключить кешированные результаты; - если вы используете драйвер MyODBC, пользовательский интерфейс (UI) имеет расширенную вкладку с опциями. Отметьте галочкой «Do not cache result» (не кешировать результат).
Также может помочь MySQL Tuner. Это полезный скрипт, который подключается к работающему серверу MySQL и даёт рекомендации по настройке для более высокой производительности.
$ sudo apt-get install mysqltuner #Debian/Ubuntu
$ sudo yum install mysqltuner #RHEL/CentOS/Fedora
$ mysqltunerMySQL продолжает «падать»
Если такая проблема возникает, необходимо выяснить, заключается она в сервере или в клиенте. Обратите внимание, что многие сбои сервера вызваны повреждёнными файлами данных или индексными файлами.
Вы можете проверить состояние сервера, чтобы определить, как долго он работал.
$ sudo systemctl status mysql #Debian/Ubuntu
$ sudo systemctl status mysqld #RHEL/CentOS/FedoraЧтобы узнать время безотказной работы сервера, запустите команду mysqladmin.
$ sudo mysqladmin version -p Кроме того, можно остановить сервер, сделать отладку MySQL и снова запустить службу. Для отображения статистики процессов MySQL во время выполнения других процессов откройте окно командной строки и введите следующее:
$ sudo mysqladmin -i 5 statusИли
$ sudo mysqladmin -i 5 -r statusЗаключение
Самое важное при диагностике — понять, что именно вызвало ошибку. Следующие шаги помогут вам в этом:
- Первый и самый важный шаг — просмотреть журналы MySQL, которые хранятся в каталоге
/var/log/mysql/. Вы можете использовать утилиты командной строки вродеtailдля чтения файлов журнала. - Если служба MySQL не запускается, проверьте её состояние с помощью
systemctl. Или используйте командуjournalctl(с флагом-xe) в systemd. - Вы также можете проверить файл системного журнала (например,
/var/log/messages) на предмет обнаружения ошибок. - Попробуйте использовать такие инструменты, как Mytop, glances, top, ps или htop, чтобы проверить, какая программа использует весь ресурс процессора или блокирует машину. Они также помогут определить нехватку памяти, дискового пространства, файловых дескрипторов или какого-либо другого важного ресурса.
- Если проблема в каком-либо процессе, можно попытаться его принудительно остановить, а затем запустить (при необходимости).
- Если вы уверены, что проблемы именно на стороне сервера, можете выполнить команды:
mysqladmin -u root pingилиmysqladmin -u root processlist, чтобы получить от него ответ. - Если при подключении проблема не связана с сервером, проверьте, нормально ли работает клиент. Попробуйте получить какие-либо его выходные данные для устранения неполадок.
Перевод статьи «Useful Tips to Troubleshoot Common Errors in MySQL»
Mysqldump is a useful tool for server owners to fully backup their databases.
However, many users come up with errors while doing a backup or restore using this tool. And, one such error is “mysqldump error 2003“.
At Bobcares, we help server owners resolve these errors as part of our Server Management Services.
Today, we’ll discuss the top 3 reasons for this error and how we fix them.
“mysqldump error 2003” – A Brief explanation
“Mysqldump error 2003” means that the network connection has been refused. And, users see the complete error message like this when using the mysqldump command.
mysqldump: Got error: 2003: Can't connect to MySQL server on 'localhost' (10061) when trying to connect
This may be due to the downtime of MySQL service, disabled network connections, and more.
“mysqldump error 2003” – Why & How to fix?
We got a clear understanding of this error. Let’s now see the main reasons for this error and how our Support Engineers fix them.
1) MySQL service downtime
This error occurs usually if the MySQL service is not running on the server. There are scenarios in which MySQL server doesn’t automatically start after server reboots. Similarly, intermittent MySQL service crashes can also cause this error.
And, users see the ‘mysqldump error 2003‘ when trying to backup/restore the database.
Solution
Firstly, our hosting engineers check if the MySQL service is running on the server. For example on Linux servers, we use the following command to check the status of the MySQL service.
ps aux | grep mysqlIf the MySQL service is down or doesn’t respond, we’ll kill the MySQL dead processes and restart the service. Moreover, we modify the server configuration to start the MySQL service automatically during server reboot.
Similarly, intermittent service crashes can occur due to resource outages, heavy traffic, DDoS attacks, corrupted data files or index files, and more. Here, our Server Experts checks the server error logs to determine where the MySQL service failed and fix that issue.
[MySQL service keeps crashing on your server? Click here to get an experienced MySQL expert to fix it for you.]
2) MySQL running on custom port
The default port of MySQL is 3306. But, server owners prefer to use a custom port to improve security. So, in such cases users should explicitly specify the MySQL port to perform database operations.
In other words, if users use a custom MySQL port and use the mysqldump command without a custom port, the MySQL server will look for the default MySQL port and throws this error.
Solution
Our Hosting Engineers use the netstat command to find the right port on which the MySQL service is listening.
netstat -lnp | grep mysqlOnce we have identified the correct MySQL port, we suggest customers to use the MySQL port explicitly in the mysqldump command. For example, see the below command.
mysqldump -u root -p password -P customport databasename > backup.sqlIn addition to that, we confirm that there are no syntax errors in the mysqldump command issued by the user.
3) MySQL socket issues
MySQL socket file is a pseudo file used by the server and clients to exchange requests and data. So, a missing socket file or wrong permissions of the socket file can lead to this error.
a) Missing MySQL socket file
The default location of MySQL socket file is /tmp/mysql.sock. In some servers, any users can delete the files in the /tmp directory which can lead to problems. We’ve seen cases where users mistakenly delete this file or create a custom cron to remove older files in /tmp folder.
Solution
Firstly, our Hosting Engineers check if the MySQL socket file that mysqladmin tries to access really exists. If not, we’ll restart the MySQL service which will create the mysql.sock file again.
Further, we protect the /tmp directory, so that the files can only be removed by their owners or root users. Alternatively in some cases, we change the default location of the MySQL socket. Similarly, if we find any cron entries removing the MySQL socket files, we’ll remove it from the server.
b) Wrong permission of MySQL socket file
Sometimes, the server has no proper access rights for the MySQL socket file or the directory that holds the MySQL socket file. If the server can’t access the socket file to communicate, it leads to this error.
Solution
Our Support Engineers correct the access privileges for the socket file and the directory, so that the server can connect to MySQL socket file for communication.
[And, do you need a MySQL Expert to look into this issue? Click here, we are online 24/7.]
Conclusion
In short, mysqldump error 2003 can occur due to MySQL service downtime, MySQL socket issues, and so on. Today, we’ve discussed the top 3 reasons for this error and how our Support Engineers fix this problem.
PREVENT YOUR SERVER FROM CRASHING!
Never again lose customers to poor server speed! Let us help you.
Our server experts will monitor & maintain your server 24/7 so that it remains lightning fast and secure.
SEE SERVER ADMIN PLANS
var google_conversion_label = «owonCMyG5nEQ0aD71QM»;
When you are working with a MySQL database, you might run into this error:
2003 - Can't connect to MySQL server on '127.0.0.1' (or some other host)
There might be several causes for that error, so you can try these methods to find out what the problem is.
1. Check for typos
A small typo in the MySQL server name, database name, username, port, etc. can lead to this error, so make sure you got them right 100%.
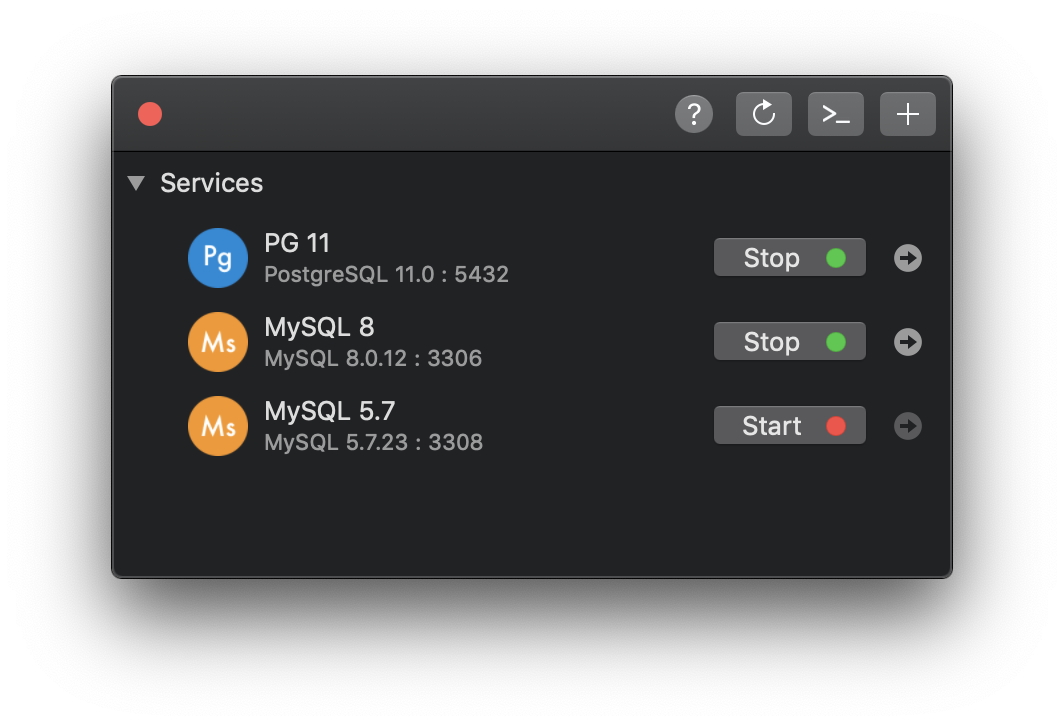
2. Make sure MySQL server is running
Maybe the problem is that there is no MySQL server running at the specified host. So the first thing you should do is to verify the status of MySQL Server. It’s recommended to try restarting the MySQL server.
You might need to check the port that it’s listening to, the default port is 3306.
If you are using DBngin to manage the local server, launch DBngin and see if the server is still on. If not, start it.
3. Connection to the MySQL server is not allowed using TCP/IP
You need to make sure that your MySQL server was not started with the --skip-networking option. You should find the setting in the MySQL configuration file (my.ini on Windows, my.cnf on Unix/Linux).
If it was, remove it and restart MySQL server for the change to take effect.
For remote connections, you need to confirm that MySQL remote access is enabled. By default, MySQL listens for connections only from localhost. Go check the MySQL configuration file and give the bind-address as the IP address of the server where MySQL service listens.
You could also try increasing the max_connection parameter in the MySQL configuration file.
4. There is a networking issue blocking access to MySQL
It could be a network firewall blocking the connection. Most often it will help to uninstall and reinstall the firewall.
5. Still no help at all?
If you tried all above and none of them worked, try connecting using SSH Tunnelling instead and see if it helps.
For more information, visit MySQL Reference Manual.
Need a good MySQL GUI? TablePlus provides a native client that allows you to access and manage MySQL and many other databases simultaneously using an intuitive and powerful graphical interface.
Download TablePlus for Mac.
Not on Mac? Download TablePlus for Windows.
Need a quick edit on the go? Download for iOS
MySQL — система управления базами данных (СУБД) с открытым исходным кодом от компании Oracle. Она была разработана и оптимизирована специально для работы веб-приложений. MySQL является неотъемлемой частью таких веб-сервисов, как Facebook, Twitter, Wikipedia, YouTube и многих других.
Эта статья расскажет, как определять, с чем связаны частые ошибки на сервере MySQL, и устранять их.
Не удаётся подключиться к локальному серверу
Одной из распространённых ошибок подключения клиента к серверу является «ERROR 2002 (HY000): Can’t connect to local MySQL server through socket ‘/var/run/mysqld/mysqld.sock’ (2)».
Эта ошибка означает, что на хосте не запущен сервер MySQL (mysqld) или вы указали неправильное имя файла сокета Unix или порт TCP/IP при попытке подключения.
Убедитесь, что сервер работает. Проверьте процесс с именем mysqld на хосте сервера, используя команды ps или grep, как показано ниже.
$ ps xa | grep mysqld | grep -v mysqldЕсли эти команды не показывают выходных данных, то сервер БД не работает. Поэтому клиент не может подключиться к нему. Чтобы запустить сервер, выполните команду systemctl.
$ sudo systemctl start mysql #Debian/Ubuntu
$ sudo systemctl start mysqld #RHEL/CentOS/FedoraЧтобы проверить состояние службы MySQL, используйте следующую команду:
$ sudo systemctl status mysql #Debian/Ubuntu
$ sudo systemctl status mysqld #RHEL/CentOS/FedoraЕсли в результате выполнения команды произошла ошибка службы MySQL, вы можете попробовать перезапустить службу и ещё раз проверить её состояние.
$ sudo systemctl restart mysql
$ sudo systemctl status mysqlЕсли сервер работает (как показано) и вы по-прежнему видите эту ошибку, вам следует проверить, не заблокирован ли порт TCP/IP брандмауэром или любой другой службой блокировки портов.
Для поиска порта, который прослушивается сервером, используйте команду netstat.
$ sudo netstat -tlpn | grep "mysql"Ещё одна похожая и часто встречающаяся ошибка подключения — «(2003) Can’t connect to MySQL server on ‘server’ (10061)». Это означает, что в сетевом соединении было отказано.
Следует проверить, работает ли в системе сервер MySQL (смотрите выше) и на тот ли порт вы подключаетесь (как найти порт, можно посмотреть выше).
Похожие частые ошибки, с которыми вы можете столкнуться при попытке подключиться к серверу MySQL:
ERROR 2003: Cannot connect to MySQL server on 'host_name' (111)
ERROR 2002: Cannot connect to local MySQL server through socket '/tmp/mysql.sock' (111)Ошибки запрета доступа в MySQL
В MySQL учётная запись (УЗ) определяется именем пользователя и клиентским хостом, с которого пользователь может подключиться. УЗ может также иметь данные для аутентификации (например, пароль).
Причин для запрета доступа может быть много. Одна из них связана с учётными записями MySQL, которые сервер разрешает использовать клиентским программам при подключении. Это означает, что имя пользователя, указанное в соединении, может не иметь прав доступа к базе данных.
В MySQL есть возможность создавать учётные записи, позволяющие пользователям клиентских программ подключаться к серверу и получать доступ к данным. Поэтому при ошибке доступа проверьте разрешение УЗ на подключение к серверу через клиентскую программу.
Увидеть разрешённые привилегии учётной записи можно, выполнив в консоли команду SHOW GRANTS
Входим в консоль (пример для Unix, для Windows консоль можно найти в стартовом меню):
В консоли вводим команду:
> SHOW GRANTS FOR 'tecmint'@'localhost';Дать привилегии конкретному пользователю в БД по IP-адресу можно, используя следующие команды:
> grant all privileges on *.test_db to 'tecmint'@'192.168.0.100';
> flush privileges;Ошибки запрещённого доступа могут также возникнуть из-за проблем с подключением к MySQL (см. выше).
Потеря соединения с сервером MySQL
С этой ошибкой можно столкнуться по одной из следующих причин:
- плохое сетевое соединение;
- истекло время ожидания соединения;
- размер BLOB больше, чем
max_allowed_packet.
В первом случае убедитесь, что у вас стабильное сетевое подключение (особенно, если подключаетесь удалённо).
Если проблема с тайм-аутом соединения (особенно при первоначальном соединении MySQL с сервером), увеличьте значение параметра connect_timeout.
В случае с размером BLOB нужно установить более высокое значение для max_allowed_packet в файле конфигурации /etc/my.cnf в разделах [mysqld] или [client] как показано ниже.
[mysqld]
connect_timeout=100
max_allowed_packet=500MЕсли файл конфигурации недоступен, это значение можно установить с помощью следующей команды.
> SET GLOBAL connect_timeout=100;
> SET GLOBAL max_allowed_packet=524288000;Слишком много подключений
Эта ошибка означает, что все доступные соединения используются клиентскими программами. Количество соединений (по умолчанию 151) контролируется системной переменной max_connections. Устранить проблему можно, увеличив значение переменной в файле конфигурации /etc/my.cnf.
[mysqld]
max_connections=1000Недостаточно памяти
Если такая ошибка возникла, это может означать, что в MySQL недостаточно памяти для хранения всего результата запроса.
Сначала нужно убедиться, что запрос правильный. Если это так, то нужно выполнить одно из следующих действий:
- если клиент MySQL используется напрямую, запустите его с ключом
--quick switch, чтобы отключить кешированные результаты; - если вы используете драйвер MyODBC, пользовательский интерфейс (UI) имеет расширенную вкладку с опциями. Отметьте галочкой «Do not cache result» (не кешировать результат).
Также может помочь MySQL Tuner. Это полезный скрипт, который подключается к работающему серверу MySQL и даёт рекомендации по настройке для более высокой производительности.
$ sudo apt-get install mysqltuner #Debian/Ubuntu
$ sudo yum install mysqltuner #RHEL/CentOS/Fedora
$ mysqltunerMySQL продолжает «падать»
Если такая проблема возникает, необходимо выяснить, заключается она в сервере или в клиенте. Обратите внимание, что многие сбои сервера вызваны повреждёнными файлами данных или индексными файлами.
Вы можете проверить состояние сервера, чтобы определить, как долго он работал.
$ sudo systemctl status mysql #Debian/Ubuntu
$ sudo systemctl status mysqld #RHEL/CentOS/FedoraЧтобы узнать время безотказной работы сервера, запустите команду mysqladmin.
$ sudo mysqladmin version -p Кроме того, можно остановить сервер, сделать отладку MySQL и снова запустить службу. Для отображения статистики процессов MySQL во время выполнения других процессов откройте окно командной строки и введите следующее:
$ sudo mysqladmin -i 5 statusИли
$ sudo mysqladmin -i 5 -r statusЗаключение
Самое важное при диагностике — понять, что именно вызвало ошибку. Следующие шаги помогут вам в этом:
- Первый и самый важный шаг — просмотреть журналы MySQL, которые хранятся в каталоге
/var/log/mysql/. Вы можете использовать утилиты командной строки вродеtailдля чтения файлов журнала. - Если служба MySQL не запускается, проверьте её состояние с помощью
systemctl. Или используйте командуjournalctl(с флагом-xe) в systemd. - Вы также можете проверить файл системного журнала (например,
/var/log/messages) на предмет обнаружения ошибок. - Попробуйте использовать такие инструменты, как Mytop, glances, top, ps или htop, чтобы проверить, какая программа использует весь ресурс процессора или блокирует машину. Они также помогут определить нехватку памяти, дискового пространства, файловых дескрипторов или какого-либо другого важного ресурса.
- Если проблема в каком-либо процессе, можно попытаться его принудительно остановить, а затем запустить (при необходимости).
- Если вы уверены, что проблемы именно на стороне сервера, можете выполнить команды:
mysqladmin -u root pingилиmysqladmin -u root processlist, чтобы получить от него ответ. - Если при подключении проблема не связана с сервером, проверьте, нормально ли работает клиент. Попробуйте получить какие-либо его выходные данные для устранения неполадок.
Перевод статьи «Useful Tips to Troubleshoot Common Errors in MySQL»
The error 2003 (hy000): can’t connect to mysql server on ‘localhost’ (10061) is an error that tells us that the connection between the MySQL client and server failed. This article will illuminate all the causes and solutions of this error message. Let’s begin!
Contents
- Why Does the Error 2003 Mysql Server Error Message Occur?
- – MySQL Service Is Not Running
- – Incorrect Login Credentials
- – Firewall Blocking Connections
- – Syntax Errors
- – Incorrect MySQL Configuration
- – The MySQL Server Is Not on the Correct Port
- – DNS Resolution Issue
- – Overloaded Server
- How To Solve Error 2003 Mysql Server Error Message?
- – Check MySQL Server Status
- – Check MySQL Service Configuration
- – Check Firewall Settings
- – Check MySQL User Permissions
- – Check Mysql Socket File
- – Correct Syntax Error
- – Local MySQL Server
- Conclusion
Why Does the Error 2003 Mysql Server Error Message Occur?
The error 2003 (hy000): can’t connect to mysql server on ‘localhost’ (10061) error occurs when there is a problem connecting to the MySQL server on the local machine. This could be because of incorrect login credentials, firewall settings blocking the connection, or the MySQL server not running.
It is important to troubleshoot the issue to determine the specific cause and resolve it accordingly.
Other reasons include overloaded server and DNS resolution issues, along with some listed below.
- Syntax errors.
- Incorrect MySQL configuration.
- The MySQL server is not on the correct port.
– MySQL Service Is Not Running
The client application cannot connect to the server if the MySQL service is not running. You can check if the service is running by opening the Services console and looking for the MySQL service.
– Incorrect Login Credentials
If the client application is using incorrect login credentials (such as an incorrect username or password), it will not be able to connect to the MySQL server. Double-check the login credentials in the application’s configuration files.
– Firewall Blocking Connections
Where there is a firewall between the client and the MySQL server, it may be blocking the connection. You can check the firewall settings and ensure the MySQL port (default is 3306) is open.
– Syntax Errors
Sometimes, syntax errors are the reason why the error arises. Therefore, you must use software tools designed to identify and correct syntax mistakes.
Some more examples include:
- Error 2003 (hy000): can’t connect to mysql server on (10060).
- Error 2003 (hy000): can’t connect to mysql server on (110).
- Can’t connect to mysql server on ‘localhost’ (10061) windows 10.
- Can’t connect to mysql server on ‘localhost:3306’ (10061).
– Incorrect MySQL Configuration
If the MySQL server is not configured properly, it may not be able to accept client connections. Check the MySQL configuration files (such as my.cnf or my.ini) and make sure that the settings are correct.
– The MySQL Server Is Not on the Correct Port
If the MySQL server is configured to listen on a different port than the default (3306), the client application cannot connect unless it uses the correct port number. Check the MySQL configuration files to see what port number is being used.
– DNS Resolution Issue
If the client application is using a hostname to connect to the MySQL server, it may be unable to resolve the hostname to an IP address. Check the client machine’s DNS settings to ensure they are correct.
– Overloaded Server
If the MySQL server is overloaded with too many connections, it may not be able to accept new connections. Check the MySQL server’s status to see if it is under high load.
How To Solve Error 2003 Mysql Server Error Message?
To solve the error 2003 (hy000): can’t connect to mysql server on ‘localhost’ (10061) error, you can start by checking if the MySQL server is running and listening on the correct port. You can also try restarting the server or checking the server configuration file for errors.
Additionally, checking the firewall settings and verifying the network connection can help resolve this error.
– Check MySQL Server Status
Ensure that the MySQL server is accepting and running connections. You can use the given command to check the status of the MySQL server:
If the server is not running, you can start it using the following command:
Sudo systemctl start mysql.
– Check MySQL Service Configuration
Check the MySQL service configuration file to ensure the server listens on the correct port and is not limited to a specific IP address. The configuration file is usually located at /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnf. You can use the following command to open the file:
Sudo nano /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnf
Check the value of bind-address and ensure that it is set to 127.0.0.1 or localhost. Also, check the value of the port and ensure that it is set to 3306, which is the default MySQL port.
– Check Firewall Settings
Ensure that the MySQL port (3306) is open in the firewall.
You can use the following command to open the port:
– Check MySQL User Permissions
Ensure that the account you use to connect to the MySQL server has the necessary permissions to access the server. You can use the below command to check the user accounts:
SELECT User, Host FROM mysql.user;
If your user account is not listed, you can create it using the following command:
CREATE USER ‘username’@’localhost’ IDENTIFIED BY ‘password’;
Replace username and password with your desired values.
– Check Mysql Socket File
Ensure that the MySQL socket file is located in the correct directory. The default socket file location is /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.sock. You can use the below command to check the socket file location:
sudo mysql_config –socket
If the socket file is not located in the default directory, you can update the MySQL configuration file to point to the correct location using the following command:
sudo nano /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnf
Add the following line to the file:
socket=/path/to/mysql.sock
Replace /path/to/mysql.sock with the correct path to the MySQL socket file.
– Correct Syntax Error
Make sure you find and correct all the syntax errors in the program. Sometimes, these are the reasons why you receive this error message. However, other types of error messages can be removed when you remove syntax errors. They are:
- Can’t connect to mysql server on ‘localhost’ (10061) ubuntu.
- Error 2003 (hy000) can’t connect to mysql server on (110) aws.
- Error 2002 (hy000) can’t connect to mysql server on ‘localhost’ (10061) xampp.
– Local MySQL Server
The phrase “local MySQL server” usually refers to a MySQL server running on the same machine that you are trying to connect to it from. If you are encountering the connect mysql error, it means that your client software cannot establish a connection with the local MySQL server.
The local MySQL server handles database requests from client software running on the same machine. If the server is not running or if it is not configured correctly, client software will be unable to establish a connection to it.
Therefore, to resolve the error, you need to ensure that the local MySQL server is running and configured correctly. You may need to check the MySQL service status, configuration, firewall settings, user permissions, and socket file location to fix the error and successfully connect to the MySQL server.
Conclusion
After reading this guide completely, you can finally understand why this error arises and how you can resolve them. Some key takeaways are:
- Error 2003 (HY000) is a common error message that indicates the failure to establish a connection between the MySQL client and server.
- The error message specifically mentions that it is unable to connect to the MySQL server on “localhost” and provides the error code “10061”.
- It occurs due to many reasons, such as incorrect login credentials, network issues, firewall restrictions, or server configuration issues.
- To resolve this error, you can try checking their login credentials, ensuring that the MySQL server is running, verifying the network connection, and checking for any firewall restrictions that may be blocking the connection.
- In some cases, you may need to modify your MySQL server configuration settings to allow remote connections or adjust the server’s listening port.
You can solve this type of error on your own by following the steps as it is in this detailed and comprehensive guide. Thank you for reading, and don’t forget to bookmark this article so that when you set to fix the error, you have everything you need!
- Author
- Recent Posts
Your Go-To Resource for Learn & Build: CSS,JavaScript,HTML,PHP,C++ and MYSQL. Meet The Team